Knee joint arthritis is a common common inflammatory-deignerative disease. Most often, this disease is observed in middle and elderly people and is the most common cause of skeletal-muscular pain in the knee joint area and disability. From this publication you will learn how to treat the arthrosis of the knee joint.
The general description
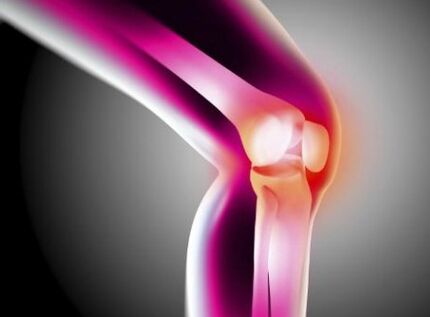
At the knee joint, the femur and the tibia are covered with joint cartilage. There is also a second type of cartilage fabric, forming the so -called mensc, which act as layers or shock absorber. The joint fluid adds additional protection and softness. Osteoarthrosis begins to develop if the cartilage that protects the bones is disturbed and damaged, as a result of which the bone surface is exposed, and the articular lubricant ceases to produce in the required quantity. In this case, complete and partial cartilage losses can be observed. This process is often isolated from a certain area in the joint, in such cases it can be caused by chronic joint damage and coating.
The deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is characterized by the process of destroying its cartilage shells. In the future, closer fabrics, such as ligaments and bones, can also include in the process. Gonartrosis, or arthrosis of the knee joint, due to the loss of cartilage, is associated with an increased stiffness and joint deformity. Bone spurs (osteophytes), which are a pathological growth of bones, can sometimes even feel externally. The bone surfaces are deformed and are not closer and do not fit with each other, as in healthy joints. As a result, the restriction of movements increases.
At the same time, the pain occurs, which is especially severe when moving after prolonged immobility, for example, in the morning, as well as at night, which eventually leads to a decrease in the quality of life. Stress can also provoke pain in the affected joint. An indirect sign of the pathological change of cartilage is the obvious narrowing of the common cavity between the femur and the tibia in the X -Ray photo.
Reason
There are several reasons for arthrosis: this is the process of aging and coating of cartilage, overweight, damage, autoimmune diseases in which immunity attacks its articular tissue, causing inflammation and its subsequent destruction. An example is rheumatoid arthritis, in which both nodes are affected at the same time and disability develops. Some experts combine concepts such as arthritis and knee arthritis, the symptoms of these diseases are similar and are often caused by the same reason.
A decrease in blood supply to the femur's head can also cause strain to strain, in this case they talk about aseptic necrosis. An inadequate formation of the knee joint in the early childhood can lead to the displacement of the mechanical shaft and the degeneration of the knee joint. Post -traumatic arthritis is secondary and develops as a result of damage to meniscus, front or posterior junction ligaments.
Symptoms
There are three degrees of knee joint arthrosis, each of which has its own signs. In the first stage, there is a slight pain, discomfort in a sore spot and periodic swelling that appears. The second degree is associated with an increase in symptoms, the appearance of cramps and a restriction of mobility. When painful sensations practically do not leave a person, and the cartilage is completely destroyed, the disease goes to the arthrosis of the 3rd degree knee.
Pain for arthritis can occur suddenly, but more often it develops slowly. A person may notice the morning pain after getting out of bed. The knees can damage when walking up the stairs, or when you need to kneel, and often the pain only appears during a walk. For people sensitive to the weather, weather changes can also cause pain in the joints.
Eiling is a consequence of inflammation, which periodically increases with arthrosis. Edema can also be associated with the formation of bone spurs or the accumulation of excess fluid in the knee. They may be more pronounced after a long period of inaction, for example, in the morning or after a long desktop stay. The skin can become reddish and hot when you touch. If chronic fusion inflammation occurs, removal of pain and edema is usually achieved by taking anti -inflammatory drugs.
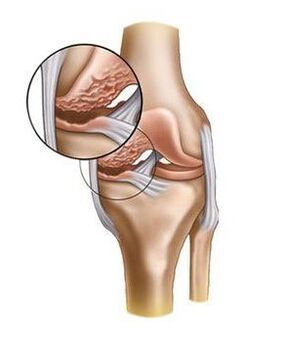
Loss of stability develops over time due to muscle weakening and instability of the entire system. Occasionally, situations arise when a person is simply unable to bend or fully direct the leg to the knee. Such a symptom is usually associated with arthrosis of the knee joint of the 2nd degree. A crisis is felt when moving because the cartilage has lost its original calm and the required amount of synovial lubrication. In the later stages, a sharp sound can be caused by the fact that bone promoters rub against each other when moving.
The limited range of movements can be seen when climbing stairs or during exercise. Many are forced to use pedestrian or reeds to move. The deformation of the knee joint is probably the most terrible symptom of arthrosis, as it shows irreversible changes in the joint, turning a person into a person with disabilities. The knees can return to one another inside as well as from the outside. Knee deformation is barely visible to significant.
Troubleshooting
The definition of knee joint osteoarthritis begins with the physical examination of the physician, the study of medical history and the conversation with the patient. Be sure to pay attention to your doctor who most often causes pain and tell us about cases of family illness, if any.
Additional diagnosis is made using:
How to treat the arthrosis of the knee joint, what medication are needed for this? Require answers to these questions further.
Principles of treatment
Standard treatment of a disease such as knee joint arthritis is primarily aimed at eliminating pain and removing functional restrictions. It is worth noting that sedatives of sedatives weaken only symptoms but are unable to affect the course of the disease and restore damaged cartilage. For treatment, narcotic analgesics, non -inflammatory drugs are used, which act slowly the preparations of gold, corticosteroids, metotoxates, etc.
Moreover, surgical intervention as well as physiotherapy and physiotherapeutic procedures may be necessary. Gymnastics with knee arthritis helps significantly in treatment, exercises are chosen by the attending physician. Despite the fact that in modern pharmacology active research and development of the most effective and at the same time safe medication for the treatment of arthrosis are developing, most medicines still have their side effects and with prolonged use disrupt the normal functioning of systems and organs.
Treatment with medication
Knee joint arthrosis therapy provides three main instructions:
In combination with physiotherapy and manual therapy, taking medication allows you to slow down the process of destruction of the articular cartilage, accelerate the regeneration of cartilage tissue and restore normal limb function.
The main purpose of medication treatment is to eliminate pain, improve cartilage food, activation of recovery processes, increase joint mobility and normalization of knee blood circulation.
Nesteroid drug
The most common for the treatment of arthrosis are such non -steroidal anti -inflammatory medicines as diclofenac, indomethacin, pyoxicam, ketoprofen and others. They are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, but long -term treatment with these drugs is not recommended, as medicines of this group have undesirable side effects, including the negative effect on the gastric mucosa and intestines, the effect of the kidney, liver and cardiovascular system. However, each medicine has its own characteristics. And recently, funds with a minimal risk to patient's health have begun to develop.
In addition, despite the need to use these tools, some studies found that NSAIDs are able to lead to a decrease in proteinoglycans production, dehydrating cartilage tissue, so such medicines should be taken strictly according to the doctor's recipe and under its control. The frequency of the side effects of NSAIDs increases with their prolonged use, which acts as a necessity for many patients with arthrosis. Experts recommend choosing anti -inflammatory selective drugs for long -term use, which have less side effects and do not have a negative effect on cartilage metabolism.

Most non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs are produced in various forms: in the form of capsules or tablets, in the form of a solution for injections and ointments or gel for external local use.
The reset of the cartilage
For eating and regeneration of cartilage in its tissues, constant consumption of compounds such as chondroprotectors - glucosamine and chondroitin is needed. These are substances useful for people suffering from knee osteoarthritis. Their reception should be performed for a very long time, from six months or more, only in this case can you rely on a positive therapeutic effect. Chondroprotectors improve the quality and amount of synovial fluid, unlike NSAIDs, they increase proteinoglycan synthesis and contribute to the regeneration of the cartilage plaque. However, due to such useful properties of these compounds, they should not be considered as the main treatment of arthrosis. Deformation of the arthrosis of the knee joint requires the use of chondroitin and glucosamine preparations for at least 1. 5 years. It is also considered that they are unable to restore a completely destroyed cartilage.
Ointments and creams
Treatment of a disease such as knee joint arthritis should include local use of gels and ointments. These dosage forms should not be supported as the only option for therapy, their use should be considered as additional to the reception of NSAIDs and chiefroprotectors. Such medicines significantly reduce discomfort, pain, swelling, improve joint mobility.
This effect is explained by the fact that penetration into the blood through the skin, ointments and creams improve blood circulation in the joints, accelerate metabolism in the cartilage and, accordingly, regenerate.
Compress
Applications for osteoarthritis have a greater effect than the application of ointments. For therapeutic compresses, the Dimexide tool is often prescribed, which has a good anti -inflammatory and analgesic effect, penetrates well into the tissue. Bishopitis is also effective, accelerating metabolic processes in the cartilage.
Injections

Inside the knee joint, the synovial fluid is very viscous, this provides the lack of tissue friction. An important part of this lubricant is hyaluronic acid, which connects proteoglycans to stabilize the structure of cartilage tissue. In patients with arthrosis, the level of this composition in the synovial fluid decreases significantly, as a result of which the latter becomes less viscous, friction increases.
Knee injections of hyaluronic acid -based drugs can slow the progression of osteoarthrosis, but only half of people with such a diagnosis receive symptomatic relief. The injection course is usually three weeks, while every seven days an injection is performed. After six months, the procedures are recommended to be repeated.
Folk remedies
Knee joint arthritis predicts an integrated approach to treatment, and recipes for traditional medicine act as additional therapy. Tools such as a decoction of onion peel, an infusion of dandelion leaves, an aloe mixture, vodka and honey in equal volumes, night compresses with honey and many others deserve attention. It is also recommended to eat more jelly and jelly.
The replacement of the union
If all of the above treatment methods did not bring the result, then the operation to replace the joint with an endoprostese. The main purpose of the surgery is to restore the natural mechanical axis of the foot and the full release of pain and discomfort. In this case, each part of the union or the entire union can be replaced. Continuous improvement of surgical equipment and the quality of implants has made such a very successful and widespread procedure.























