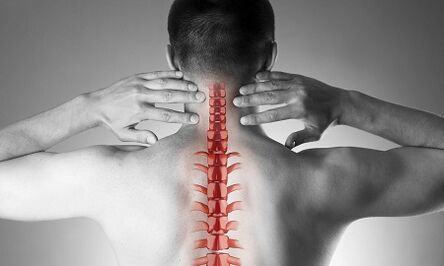
Cervical osteochondrosis, or spondylosis, occurs as a result of changes in the shape and structure of the vertebrae.Despite the fact that the cervical region is short enough about the total length of the spine, is probably the most important part of the spinal column.Each pair of neighboring beads forms the intervertebral holes through which the nerve roots go and go to each muscle and organ of the upper half of the body.Through other holes - in the lateral processes of these beads - vital vessels provide blood supply to the brain.
Causes of cervical back osteochondrosis
The causes of osteochondrosis are:
- damage
- "Sitting" work on the monitor located below the eye level,
- Physical work associated with weight transfer,
- Long -term stay by driving a car,
- Work "on the phone" without the use of remote devices (in this case, the operator prints the phone on the ear shoulder)
- Constitutional features (crooked, congenital changes in cervical vertebrae, short neck)
The formation of pathological vertebral changes
With osteochondrosis, small spots begin to form at the edges of the vertebral bodies, which can damage the structures located nearby.Most often, this occurs in response to an excess load on the cervical separation, and is not only the result of "aging" of intervertebral joints (remember that it is used to be considered degenerative osteochondrosis, then a natural "age -related" disease, such as osteoarthrosis).As the disease develops, closing plaques of vertebrae occur and a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs.These discs are normal play the role of shock absorber between the beads, and, among other things, prevent spinal root damage.With progressive osteochondrosis, a prolonged core of the intervertebral disc jacket occurs, on which there is more and more pressure during the disease while weakening the "restriction" of ligaments from all sides.This hernia is also capable of squeezing spinal structures and cause neurological manifestations of the disease.
What are the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with pain syndrome
Any neck pain forms the pathology of the cervical back.In terms of growth, the intensity of the pain syndrome is divided into 4 stages, the first patient feels numbness, tingling, a feeling of "tightness" in the area of a particular muscle group, in the fourth stage - the most severe - the pain is so severe that they lead to the patient's motion and loss of performance.
In addition to the pain syndrome in the cervical region and occipital, the patient marks "reflecting" pain in the upper limb, the lateral areas of chest submission.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with radicular syndrome
They talk about involvement in the process of nerve roots when pain, numbness and tingling feels spread to the lower jaw, upper back, forearm and fingers.At the same time, the patient draws attention to the fact that he "seemed to be leaving" his hand, he slept inappropriately.Morning stiffness is observed in the fingertips, which lasts no more than 10-15 minutes.With the development of radicular syndrome, during examination, a decrease in the strength of the muscles of the upper extremities may be observed.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with "vertebral artery syndrome" syndrome
Regarding the involvement in the blood vessel process (squeezing them with hernial extensions or osteophytes), they say when the patient complains of frequent headache attacks, especially after a long stay in a certain position when he is thrown from his head (for example, when swimming with a brass), if the noise is worried.This clinical situation is well detected using ultrasound (with "Doppler map mode").With ultrasound, the inquisition of vertebral arteries is determined, the narrowing of their lumen.In this case, we can talk about surgery, as a significant change in blood flow to the vertebral arteries is a risk factor for the development of stroke.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with "cardiac syndrome (heart)"
This syndrome forces the patient to contact mainly the cardiologist, as the main complaints relate to pain in the left half of the chest, the subchapular region, which weakens or intensified when physical activity or body position is performed.After excluding myocardial infarction and other cardiac disease, the patient encounters the observation and treatment of a neurologist and orthopedics.
Troubleshooting
To clarify the diagnosis, four methods are used: radiographs, ultrasound, calculated tomography and magnetic resonance imaging images.
The most affordable method is still cervical back radiography, the most informative is radiography in the side projection ("side view").This method allows in the first approximation to determine the presence of damage, gross structural changes in the beads.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is performed to clarify the condition of the vertebral arteries.With the help of this method, they find out if the blood flow is disturbed, and if so, to what extent and what kind of obstacles were raised and where they are localized.
Calculated tomography (CT).This allows you to evaluate the state of bone structures more accurately, the degree of bone density allows you to see smaller osteophytes (bone results) than possible with X -Ray.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images.This type of examination is indispensable for suspected hernias, accurate localization of spinal cord damage and the extent of this damage.This study is needed if the question is asked from the surgical treatment of the cervical back disease.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Treatment
The standard group of products for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis reflects the purpose of treatment: relieving pain syndrome, removing painful muscle spasm and inflammation of the nerve roots, increasing spinal mobility.To achieve these goals, mainly the use of painkillers, NSAIDs -non -inflammatory non -steroidal anti -inflammatory, muscle relaxants are used.It should be remembered that self -medication from these groups can be dangerous, as there is a possibility of incorrect interpretation of symptoms, as well as underestimating the side effects of these medications.Local medicines (Basel) from NSAIDs in the form of gel are widely used, and if the pain stops, the same medicines can already be used in the form of ointments.
For the treatment of osteochondrosis at a deeper, "underlying" level, systemic medicines are used.These substances restore vertebra cartilage structures, prevent their further damage.Treatment courses are long, the effect persists for many months.
Cervical osteochondrosis has significant changes from spinal pathology.Neck pain in this case may not be provoked by signals by the spinal nerves they suffer, but by painful overload of chronic muscle - all together is called muscle syndrome.This is a fully "benign" condition, which is well treated with the same set of medicines: non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, using intramuscular "blockade" using steroids.Usually, the doctor detects a sharp pain when investigating the so -called "trigger" points along the entire cervical back as well as in the upper shoulder band muscles.Most often such a pathology occurs in women, mostly younger than 40 years.Despite the pronounced pain syndrome, the vascular-nore structures remain intact, the blood flow of the head area does not suffer.
Manual therapy
This method of treatment can be effective to give birth to recently (often as a result of a minor damage, subluxation) neck pain, not accompanied by dizziness, other changes from the nervous system and the circulatory system.It is permissible to address manual therapy only after a thorough examination, in addition, the doctor who performs this procedure should have sufficient experience in the field of traumatology and orthopedics.With "old" forms of the disease, the use of manual therapy is dangerous!
Two methods of this type of intervention are known:
- Manipulation (sharp influences of considerable force aimed at eliminating subluxation, "known bone clicks");
- Mobilization (the method is based on a smooth extension of the neck after heating and relaxing the neck muscles).
A combined method based on a combination of two main ones is also used.It is important to remember that in addition to these contraindications, manual therapy is forbidden for any disease, associated with an increase in blood pressure, for any pathology of the thyroid gland and ENT or ENT-Organ.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home
Medical gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis
The first and main rule for beginners to be included in physiotherapy exercises is not to perform exercises, overcoming painful sensations.Of course, you should not start in the "acute" period when the pain has just appeared.Another important recommendation is to avoid sudden movements and circular movements in the cervical region.
Each lesson should start with a self -massage of short neck muscle light.
Below is a warm warm "heat":
- The hands sit along the body, the shoulders are equal, the back is straight (you can control the behavior with slightly soles, shoulder edges and buttocks on the wall).We walk in 1 minute place all over the foot, 1 min - in socks, 1 min - on the heel.
- The starting position is the same.We squeeze the brushes into the punches, raising the shoulder landing, our hands are directed.The movements are slow, we make 20 repetitions, the last lift is more than 5 seconds.We make sure the neck muscles are not "caught".
- The starting position is the same.We bend the heads from the right side, then on the left side.The movements are polished, a slope in 8 accounts, at the extreme point of trend - hold for 8 seconds.
- The starting position is the same or sitting in a strong chair.Smooth heads of the head forward, at the extreme point - keep for 8 seconds
- The starting position is the same or sitting in a strong chair.Slowly bending your head forward, up to the chin to the chest, then slowly turn your head to the right (in 4 accounts) and to the left (in 4 accounts).Do not allow muscle strain.
- The starting position is the same or sitting in a strong chair.We raise the shoulders to 4 accounts, then we also lower them to 4 charges.10 repetitions.
- The starting position is the same or sitting in a strong chair.We raise your shoulders, but now we perform circular movements forward, 8 accounts.10 repetitions.
- We line up, control behavior.In 4 accounts, we reduce the shoulder blade behind our backs, trying to tie them, at the last point we continue for 8 seconds, then return to the starting position.
Pillow
As already mentioned, neck muscle hypertonitis is the first and often the main reason for the development of cervical osteochondrosis.A rational selection of pillows and mattresses, providing a quiet and comfortable position during sleep is no less than gymnastics, physiocytes and drugs.
When choosing a mattress, pay attention to the composition of the filler (the products are suitable, at least half made of the chip of the coconut nut nut, that is, having a sufficient degree of rigidity).Small spring mattresses do not provide sufficient spine adjustment.The most optimal sleep for sleep is on the side, attracts one or both knees in the stomach.The pillow should be set in such a way as to fill the entire space between the shoulder, the ear and the mattrates, the parietal part of the head is in the same horizontal line as the spine.To avoid too high and very low, as well as soft pillows.The ideal option is a product of an ergonomic shape, that is, in this case, with a small squeeze on one side.
General recommendations
Pay attention to behavior.During walking or in a standing position, the position is a position when the chest lasts forward and the stomach is pulled.
Avoid long -term stay in a sitting position.A simple rule for preventing cervical osteochondrosis is known: after every 60 minutes of work, a 10-15 minute walking or heating period is required.
A chair for work should have a high head or back.
In a sitting position, the legs should stand on the floor, and the neck should not be tense.For this purpose, use special orthopedic devices: rollers under the neck when driving in a car, a pillow under your back.
Avoid lifting weight.If necessary, kneel down, press the heavy object on the body and then stay well using the muscle strength of the leg, but not the "push" of the back.
Do not be supported with pointed legs.Use stands, work surfaces in order to bring the object closer to yourself, and not convince your face on the subject.Try to do homework sitting in a chair or gymnastics.
If you need to use a shovel, broom or rake, do not strain your arms, back and neck, do not support.
Avoid bronze -style swimming.























